Anemia
The purpose of red blood cells in the body is to deliver oxygen from lungs to other parts of the body using a protein called hemoglobin. Anemia is a disorder where the cells do not receive adequate oxygen from the blood. It is mainly due to not having enough number of red blood cells (RBCs) or sufficient quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. Anemia can be from various causes. The most common causes include loss of blood because of continuous bleeding, iron deficiency, kidney diseases, stomach ulcers, pregnancy, poor nutrition, abnormally low production of RBCs, excessive destruction of RBCs.
Anemic patients generally experience tiredness and lethargy (a feeling of laziness). It is not uncommon to have their mental state affected as well. Headache, poor concentration, malaise, increased sweating are some of the symptoms linked to anemia. In some cases, anemia is temporary and caused by nutritional deficiency while in others it may result due to inherited conditions. However, severe anemia can be life threatening.
Vital Tests
- Ferritin
- Iron
- Serum Folic Acid
- Total Iron Binding Capacity
Autoimmune Disorders
A healthy human body has a powerful immune system to resist the invasion of pathogens or micro-organisms. Unfortunately, sometimes, the immune system wrongly recognizes its own cells as foreign and attacks the body itself. These misdirected immune responses are referred to as autoimmunity which is characterized by the presence of any antibodies against host-antigens.
The origin and mechanism of autoimmune diseases is still largely a mystery. Autoimmunity seems to result from the interplay of various influences, including environmental and genetic factors.

There are many different types of autoimmune disorders. Based on the part of the body affected, autoimmune diseases are classified as organ specific (eg. Type 1 diabetes) and non-organ specific (e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus). In organ specific diseases, the lesions are restricted to an organ as an antigen present in the organ triggers autoimmunity. However, in systemic autoimmunity the antigens are ubiquitous.
An autoimmune disorder may result either in the destruction of one or more types of body tissues or changes in the organ functions. Its symptoms may vary depending upon the disease and location of abnormal immune response. The goal of treatment in autoimmune disorders is to reduce the symptoms by controlling the autoimmune responses and retaining the body's ability to fight diseases. So far, there is no prevention for most of the autoimmune disorders.
Vital Tests
- Anti Sperm Antibody
- Complement 3
- P-ANCA (C-ANCA)
- Anti-ds DNA
Cancer
Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues of the body. Under normal circumstances, there is a balance between cell proliferation and programmed cell death, which is tightly regulated to ensure the integrity of organs and tissues. Disruption of this physiological process leads to autonomous uncontrolled division of cells in the body called 'Cancer'.
This uncontrolled cell division in cancer leads to the formation of lumps or masses of tissues called as tumors. Certain types of tumors that stay at one spot and has limited growth are generally considered to be benign whereas the tumors that proliferate and spread to other systems of the body thereby adversely affecting the body functions are malignant. There are many different types of cancers and each cancer is classified based on the type of the affected cell.

Cancer is a rapidly growing challenge to the world. Anyone can get cancer but there are certain risk factors that may make it more likely to happen, risk factors smoking, alcohol consumption, previous family history of cancer, HIV infection, exposure to harmful radiations, asbestos fibers and some hazardous chemicals used in workplace.
The symptoms and treatment of cancer always depend on the type of cancer and how advanced is the cancer. The earlier the cancer is diagnosed, the better one's survival rate would be. Today, cancer can be detected in many ways which include physical examination, screening tests, and medical imaging and nuclear medicine scans.
Vital Tests
- Alpha Feto Protein
- Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
- Thyroglobulin
- CA-125
- CA 15.3
Cardiovascular Disorders
Cardiovascular disease is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. Most people think of only middle-aged and old people of being affected by heart diseases. But nowadays because of the sedentary lifestyle, individuals from any age group are likely to develop cardiac diseases. They have become one of the largest causes of death worldwide. Age, gender, high blood pressure, high serum cholesterol levels, smoking, alcohol consumption, family history, obesity, lack of physical activity and diabetes are the risk factors associated with developing cardiovascular diseases.

Practicing healthy living habits at the early age such as following a routine exercise schedule, going for a brisk walk, refraining from smoking and alcohol consumption, having a healthy diet, keeping cholesterol levels low and maintaining a correct weight would greatly diminish the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
In general, heart diseases are related to a process called atherosclerosis, a condition that develops when a substance called plaque builds up in the walls of the arteries due to high cholesterol levels. It narrows the width of the artery and obstructs the flow of blood. If there is a clot in the artery, it blocks the blood flow and results in a heart attack or stroke. Some of the other cardiac disorders are heart failure (failure of heart to pump enough blood to the body), arrhythmia (abnormal rhythm of heart), heart valve problems etc.
With advances in medical science, today most of the heart diseases are easier to detect and eventually treat. A marked reduction in the mortality due to cardiovascular disease has been observed in the past few years.
Vital Tests
- Apolipoprotein A
- Apolipoprotein B
- C-Reactive Protein
- Lipoprotein
- Homocysteine
Diabetes
Diabetes is not a disease but a disorder, affecting more than 10 % of the human population where the body either does not produce adequate insulin or the insulin produces is not properly utilized, due to which the glucose concentration remains high in the blood stream.
Like any engine, our body needs fuel to keep it going and this fuel is glucose. Glucose is derived from all sorts of foods that we consume, from chocolates to chicken, from bhelpuri to burger, food is converted to glucose which is in turn converted to energy for body functioning.

After every meal our food is converted into glucose, thereby increasing the blood glucose levels. The blood glucose levels are controlled by a hormone called insulin. The cells cannot use glucose without the help of insulin. In a normal individual, the body manages to maintain an ideal level of glucose concentration. But in diabetes, insulin is either not produced or not utilized properly, and hence the glucose remains in the blood causing the condition, "Diabetes".
Vital Tests
- HbA1c
- Insulin
- Lipid Profile
Infertility
Infertility refers to biological inability of an individual to conceive. There are many possible causes of infertility. Some can be easily diagnosed and treated while others cannot. Factors that can cause or contribute to infertility are hormonal imbalance, diseases like gonorrhea or chlamydia, use of certain drugs, medical conditions such as diabetes or thyroid diseases, use of tobacco, marijuana, alcohol and many more.
The signs of infertility are not the same for all individuals. There are several diagnostic measures that can help detect the condition. Usually, hormonal imbalance is the most common cause of infertility and it can be detected relatively quickly and easily through testing of blood and urine samples and can be treated by medications or infertility treatments such as ovulation induction and invitro fertilization.
Vital Tests
- Estradiol
- Progesterone
- Testosterone
- Luteinizing hormone
Infectious Disease
Infectious diseases are a result of infection because of the presence and growth of microorganisms. There are several infectious diseases that have taken a toll of many innocent lives in the past and prevails today as well. Despite several intensive efforts, these life threatening infections occur over time because microorganisms are constantly evolving and gaining resistance to the existing medications. Moreover, in a highly populous nation like India where is exposure to unhygienic conditons is common, infectious diseases readily spread amongst the population.
The problem becomes more serious because many who contract these diseases are unaware without timely diagnosis of the condition since these are predominantly asymptomatic.
There is a plethora of infectious diseases such as hepatitis, HIV, dengue, rubella, leptospirosis. Some infectious diseases can be passed from one person to another. Some, however, are transmitted via bites from insects or animals. Others are acquired by ingesting contaminated food or water or other agents in the environment. The signs and symptoms of diseases vary but often include fever or shivering.
Various infectious diseases continue to emerge and re-emerge over the time thereby have a profound impact on the economic development. This necessitates the establishment of an effective public health system to overcome new unexpected infectious diseases.
Vital Tests
- Dengue IgM
- Herpes simplex virus I - IgM
- Leptospira IgM
- Rubella IgG
- Toxoplasma gondii IgG
- Hepatitis B Envelop Antigen
Thyroid
Thyroid is a large butterfly shaped gland situated in the front part of the neck, just below the larynx (voice box). Being a ductless gland its hormones are secreted directly into the bloodstream. Triiodothyroxine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), the two thyroid hormones. They help in keeping the body active physically as well as mentally, maintain body temperature and energy levels, fluid balance, cardiac rate when produced normally. But their production is regulated by Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) secreted by the pitutary gland.
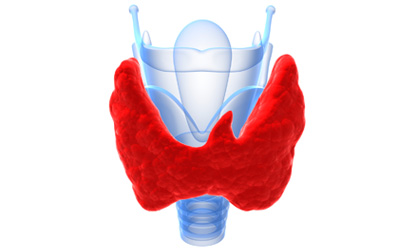
When the thyroid gland does not function properly, it can have an impact on every aspect of our health, and in particular, weight, mental state, and energy levels. Some of the symptoms that signal the possibility of thyroid problems are obesity, depression, anxiety, hair loss, heart disease, sexual dysfunction and infertility. The symptoms may be mild or often be confused with other problems which is why many patients remain undiagnosed and untreated for a long time.
Generally, individuals with a family history of thyroid problems, abnormal menstrual history, high cholesterol level and those who feel exhausted and fatigued or women above 40 years of age are more likely to have thyroid problems. It is therefore essential to have thyroid function tests to rule out any possibilities of thyroid abnormalities.
Vital Tests
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Total Triiodothyronine (T3)
- Total Thyroxine (T4)
- Free Triiodothyronine (FT3)
- Free Thyroxine (FT4)